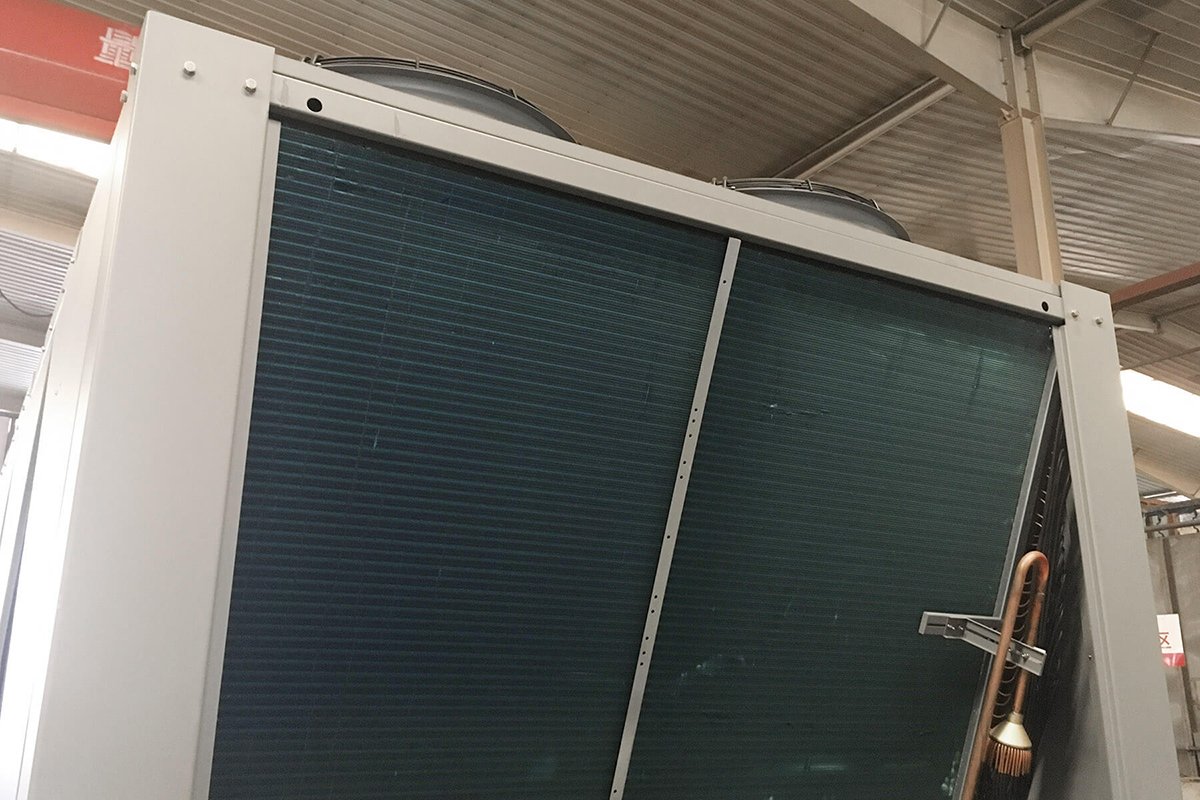
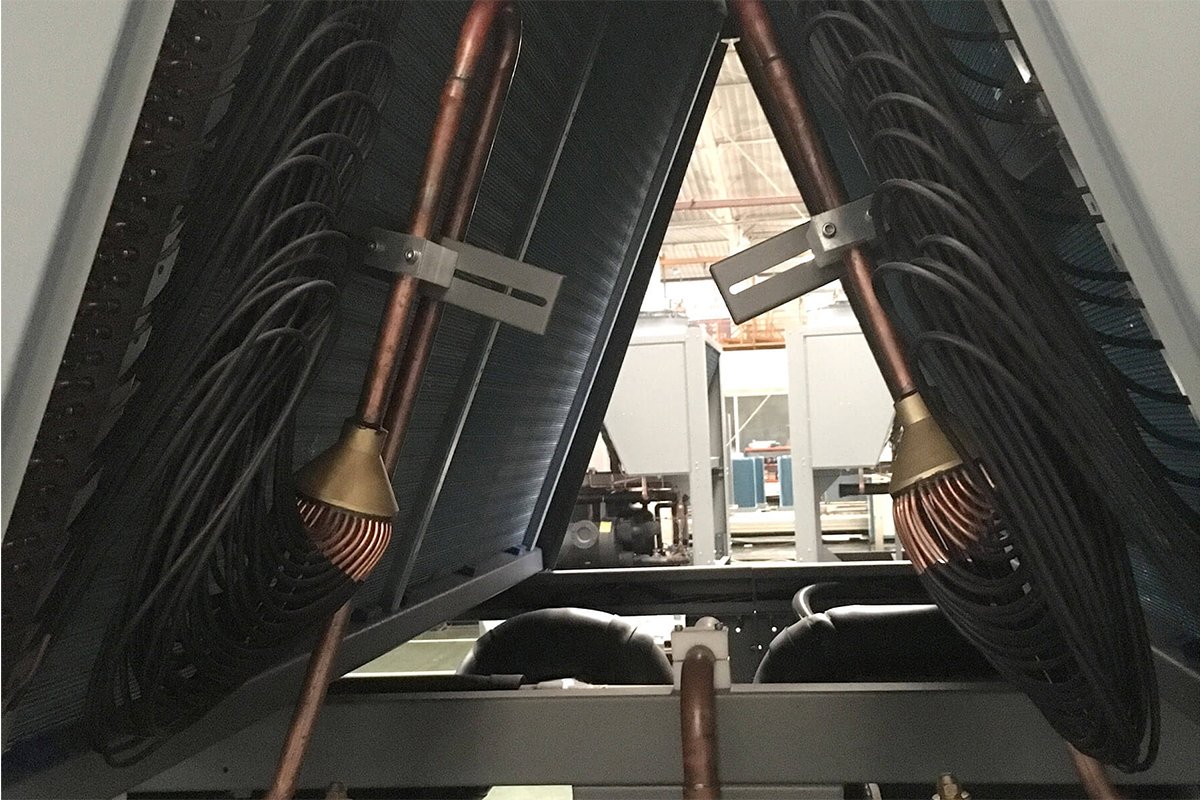
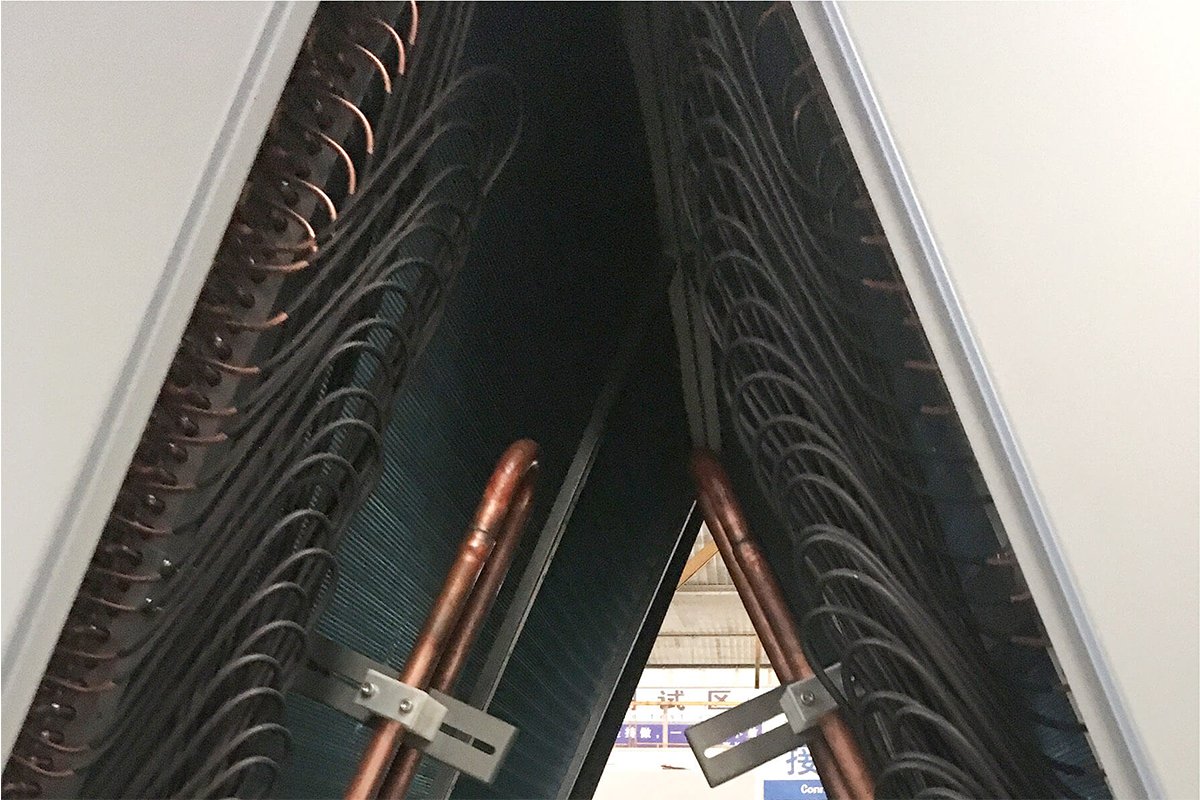
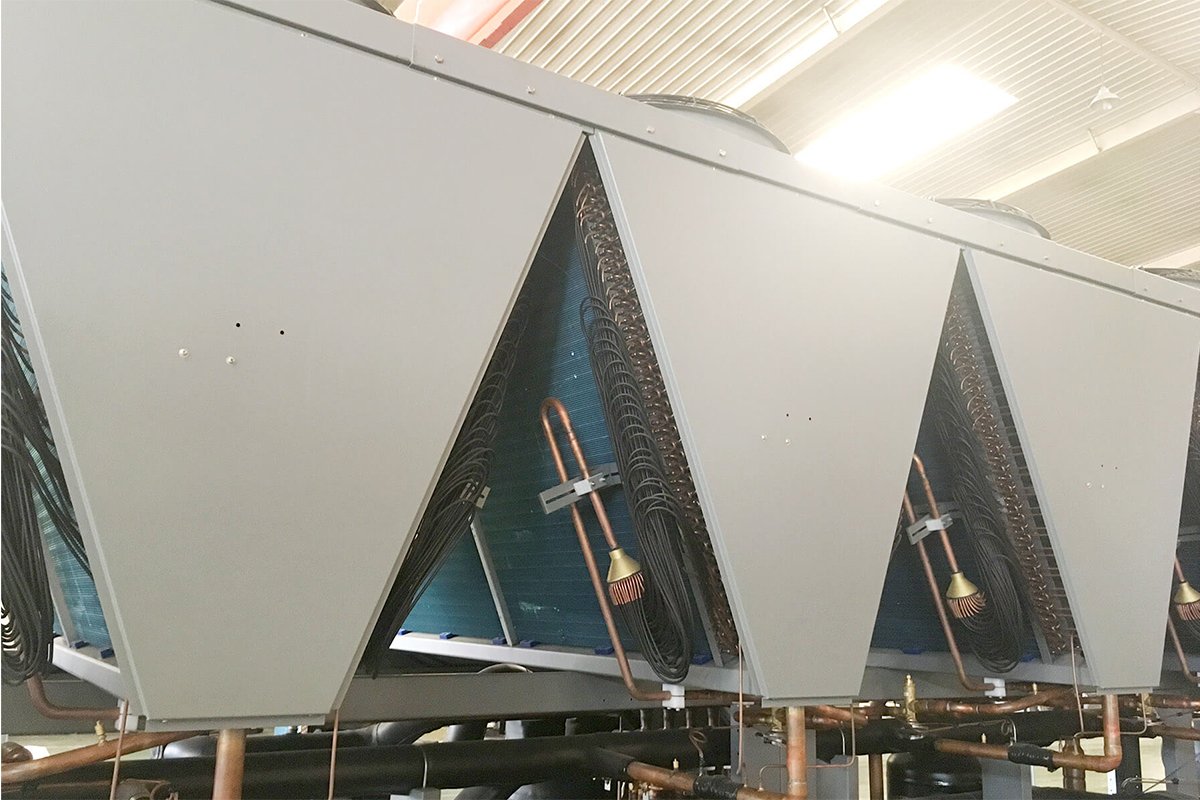
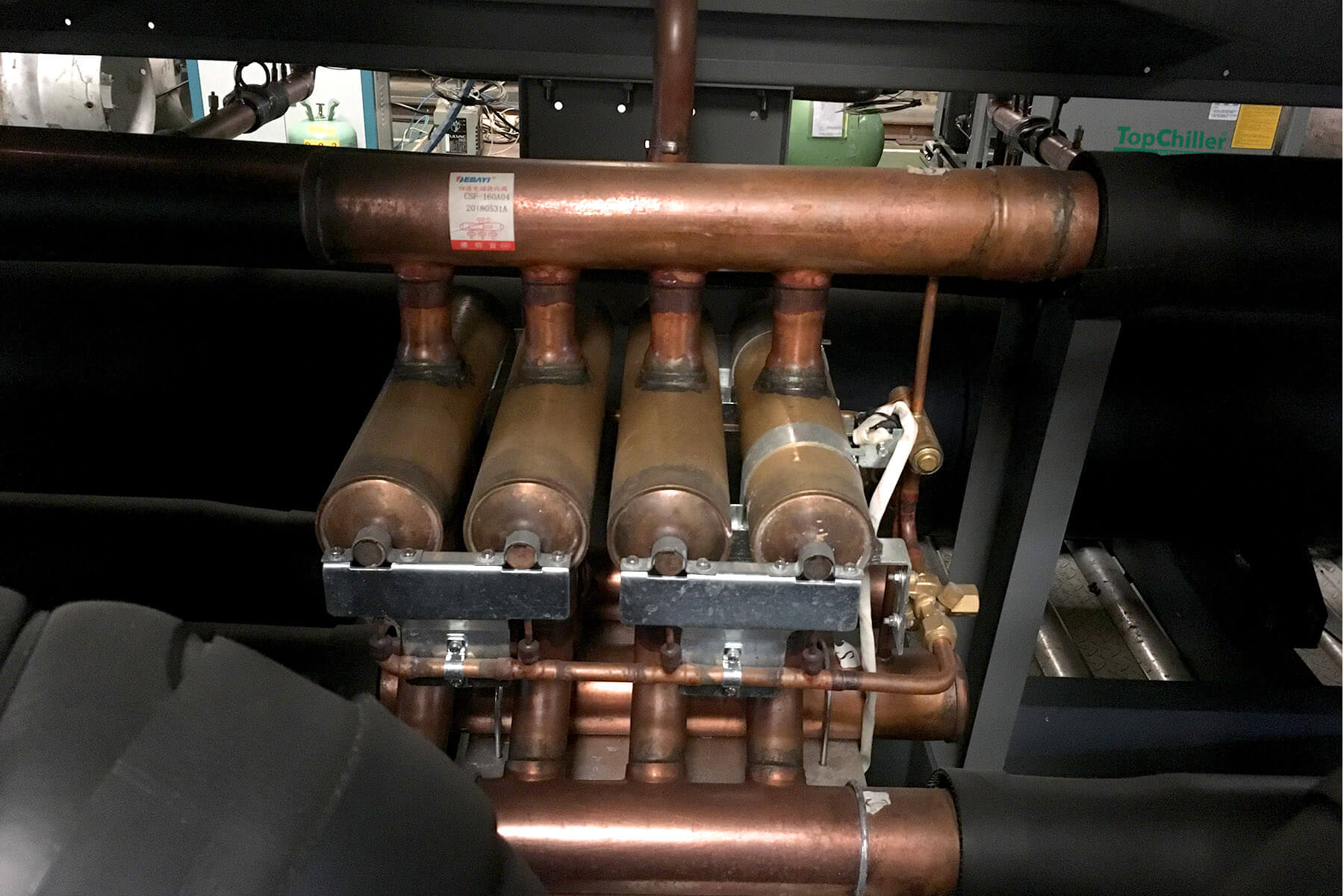
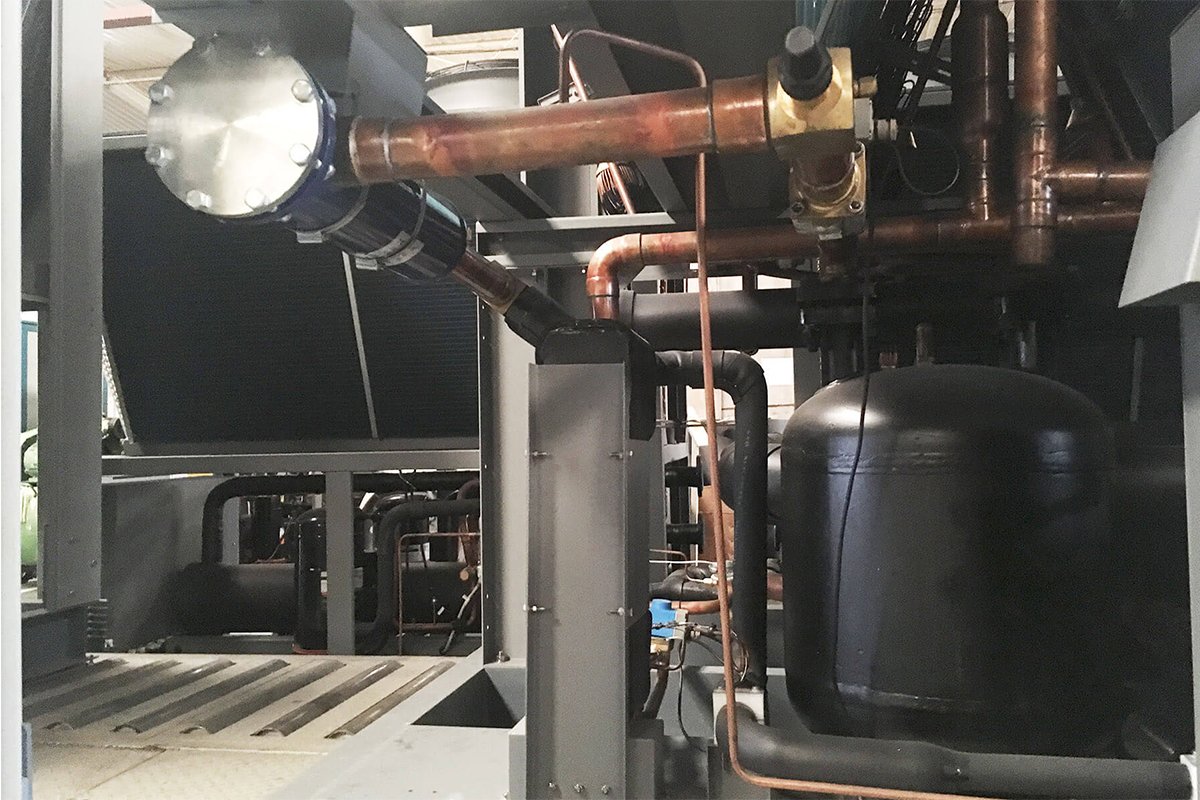
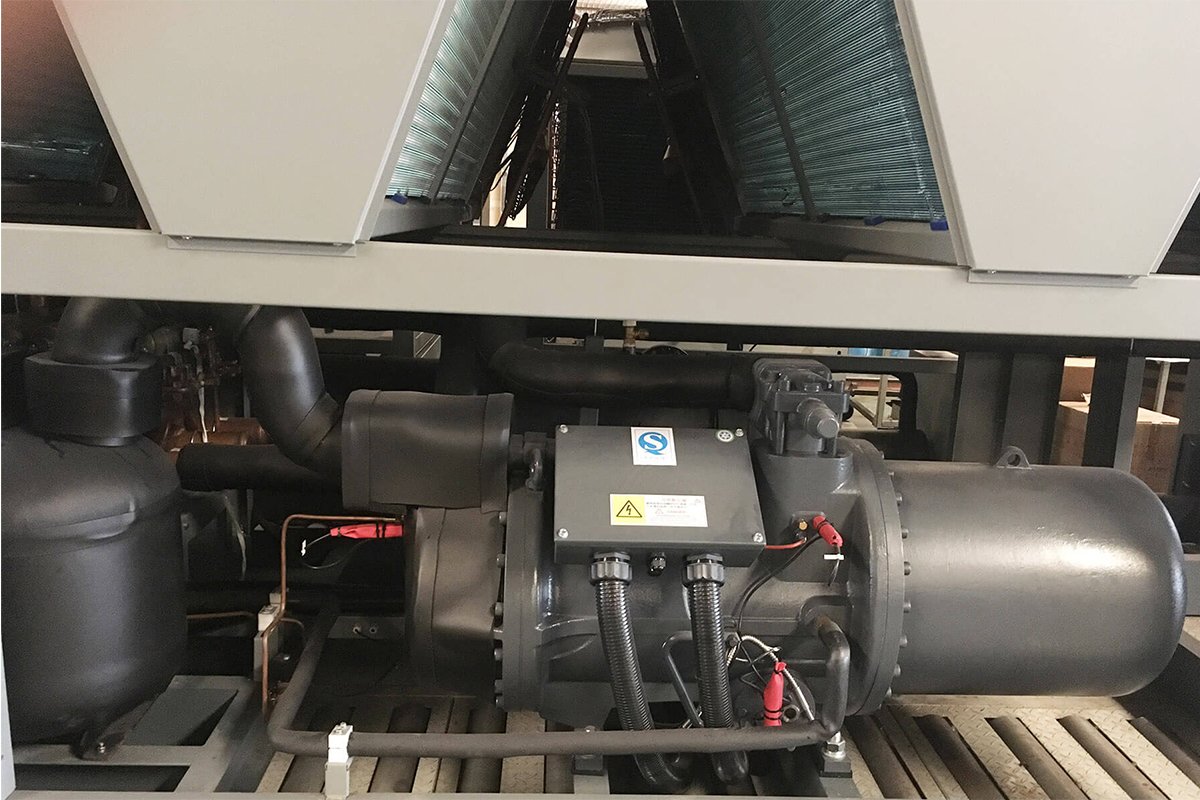
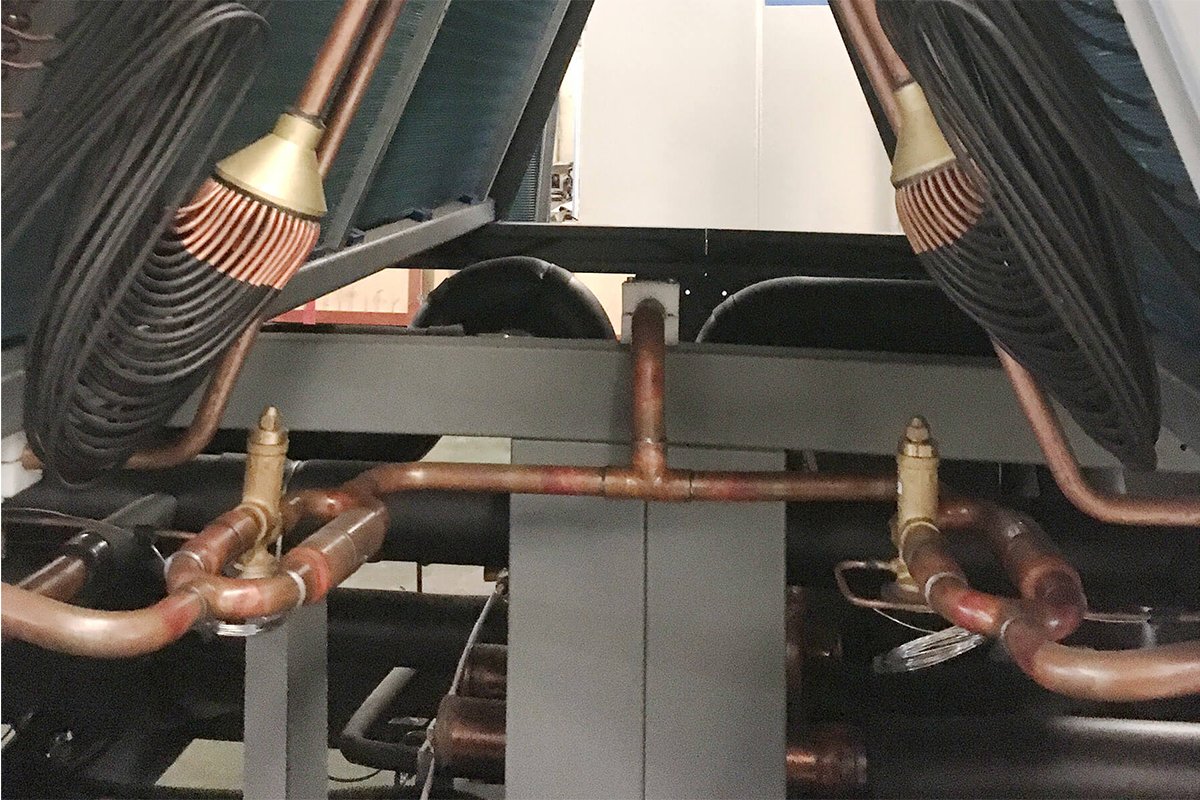
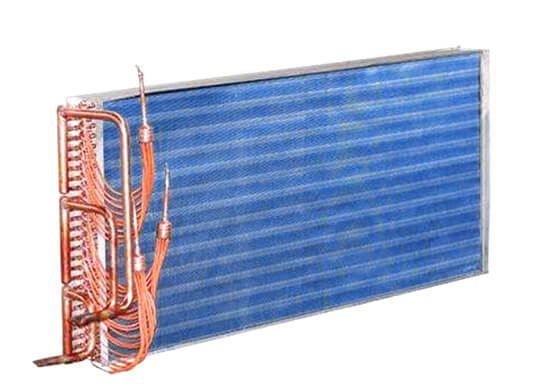
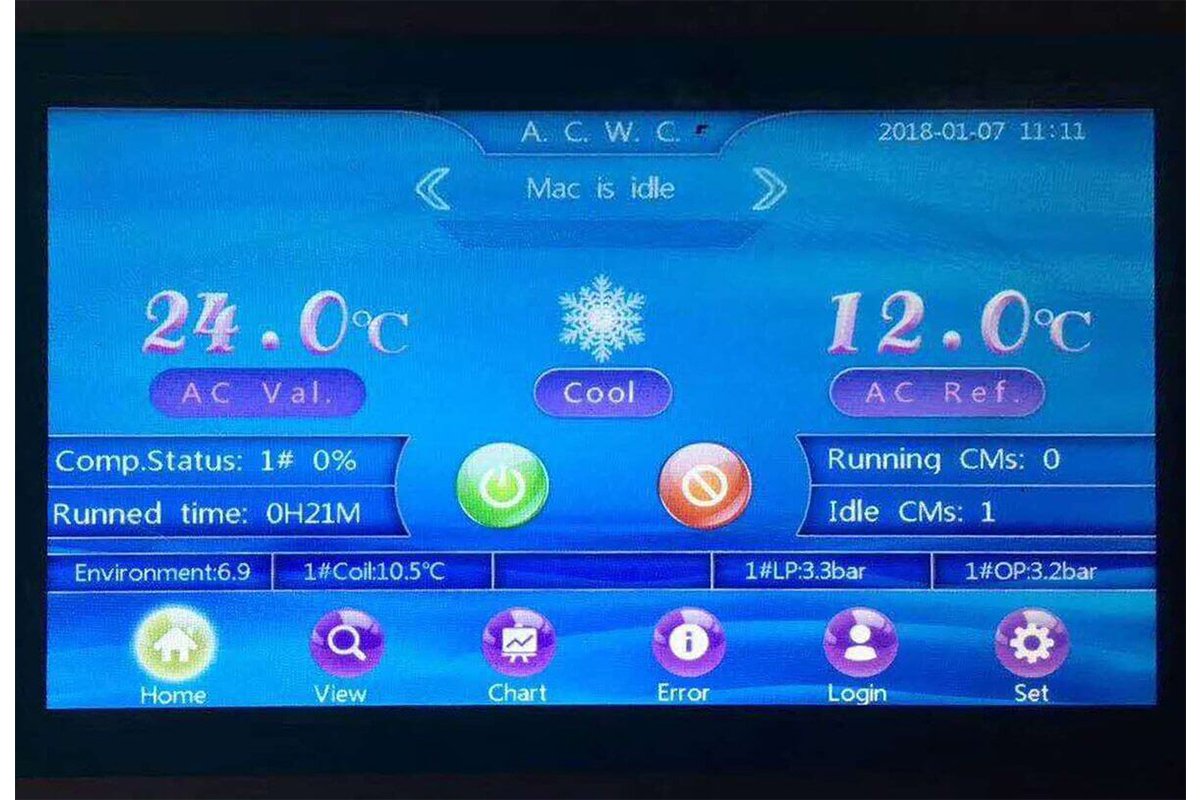
TopChiller can design and manufacture all types of chillers for you
- Cooling capacity ranges 1 ton -500 ton
- Temperature control ranges -35℃/+35℃
- Worldwide brand high-quality compressor
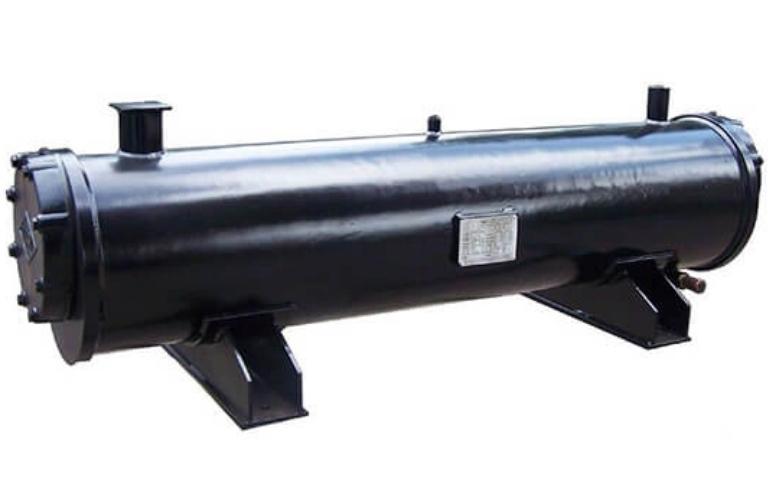
- Shell and tube heat exchanger
- Brazed copper piping & hot gas bypass
- Job-specific evaporator for diverse application
- Dual circuit efficient condenser & PLC controller
- Compact design with mounting pads or asters
Your Premier Chiller Manufacturer and Supplier in China Over 20 Years
A Chiller is a cooling device that is constructed to regulate the temperature of machines, industrial processes, and product stability by use of chilled water/air/oil or glycol circulation based on a refrigeration and compression system.
TopChiller is an exemplary company in China that is manufacturing steady, environment-friendly, efficient Chiller and proficiently supplying around the world since 1999.
With twenty years of innovative experience and research, TopChiller is enabled to customize the contemporary requirements of our customers by manufacturing a wide range of different Chiller models for different applications.
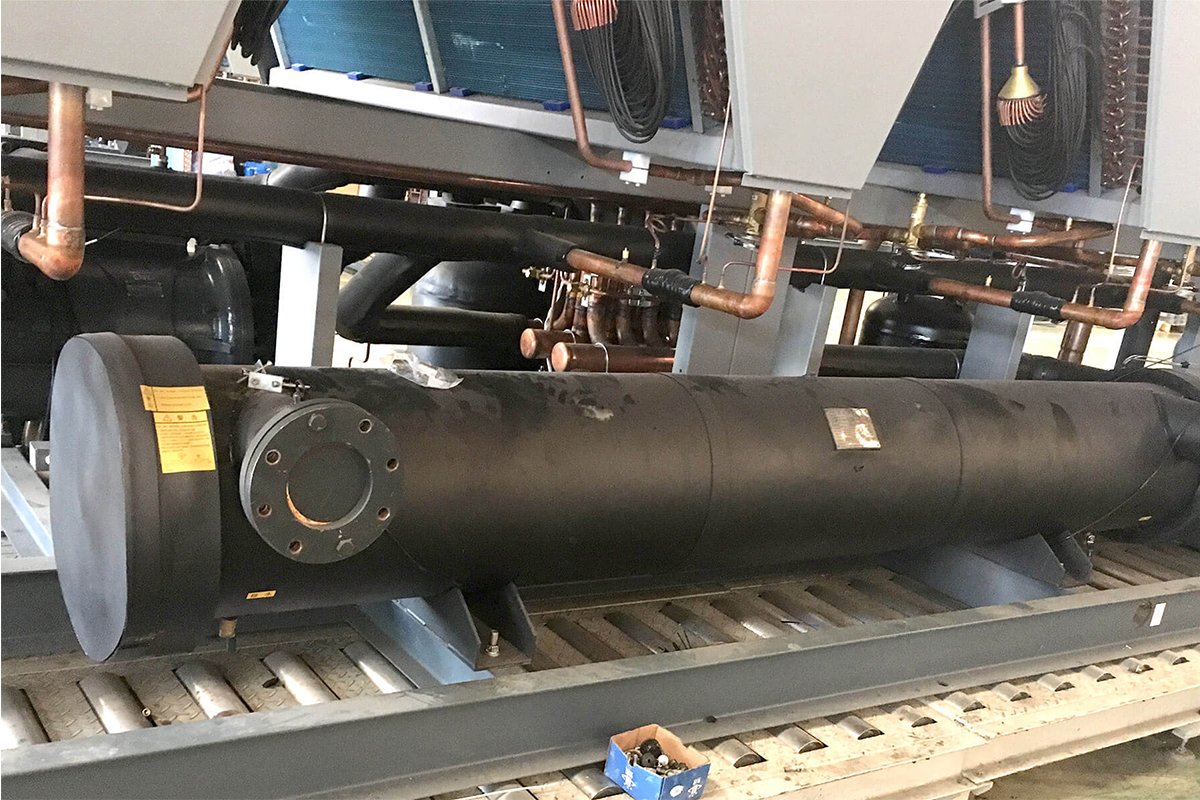
TopChiller brand Chiller is constructed with a variety of components for durable working as an evaporator, single or dual compressor, brazed plate heat exchanger, protecting devices, temperature controller, control panels, expansion valves, water tank, and power supply.
Chiller designed by TopChiller has a variety of features and benefits as given below.
- TopChiller brand Chiller is highly stable and straightforward in its performance configured by the simple design of tubes, coils, and tank installation preventing the accumulation of scales and dust particles with cleaning.
- The energy-efficient Chiller prevents the accumulation of heat produced during industrial processing featured by the installation of a reservoir and refrigerant pump releasing heat by chilled refrigerant circulation.
- TopChiller engineered Chiller is installed with different cooling refrigerants depending on the nature of application temperature requirements configuring cooling by compression and refrigeration phase-change process (from chilled liquid to gas and gas to liquid).
- Dual condensers are installed inside the Chiller providing versatility for choosing the unit according to ambient temperature as the air-cooled condenser releases heat by chilled air and the water-cooled condenser uses water for chilling purposes.
- TopChiller designed Chiller has stainless steel compact design that prevents the unit from corrosion and ensures easy outdoor installation.
TopChiller engineered Chiller is highly versatile and used for a variety of industrial applications as given below:
Fermentation industry, food, and beverage industry, plastic processing, laser industry, welding, injection molding, dye casting, explosion industry, chemicals processing, drugs manufacturing, medical industry, and plating, etc.
If you are desiring to have Chiller for your application with distinctive features, superb reliability, and long service life?
If you are in a quest to select the most famous and trustworthy company manufacturing energy-efficient Chiller for the establishment of your business by getting creative ideas and incisive guide?
You are directed to an exact destination. TopChiller is the most experienced and collaborative company in China. Go for a call or arrange a meeting with TopChiller experts and professional engineers to get a buying guide and assistance for your application.
Our experts will help our clients to customize a Chiller according to your requirements with quality assurance at handsome charges.
General Description:
A Chiller is an efficient cooling unit that uses refrigerant to circulate heat between evaporator and condenser. It discharges unwanted heat of application by chilled air/water circulation. To prevent heat-generating equipment from damage or failure, you need a Chiller that consolidates heat rejection and durability.
Different types of compressors as a scroll, screw, reciprocating and centrifugal, air/water-cooled condensers, shell and tube type/brazed plate heat exchanger, and expansion valves are its core components.
TopChiller fabricates premium quality Chiller with a rapid response control system, emergency alarms, power supply, and flow switches for unit regulation.
Based on compressor and condenser type, the TopChiller brand has introduced an assorted number of Chillers for different processing applications as:
Injecting molding, chemical processing machines, fermentation, semiconductors manufacturing, plastic industry, lasers, laboratories, hospitals, metal cutting, anodizing, milling, plating, etc.
TopChiller is an innovative manufacturer and supplier that offers stable and efficient air and water cooling solutions for industrial applications by designing a full line of Chillers.
Under ISO qualification, CE certification, and long-term working experience, the Chiller designed by TopChiller are exported over the global world.
To avail of our services today by confirming your order at a suitable price by making a phone call or email. Our sales team is directed to ensure your satisfaction from every aspect.
Features and Advantages:
The unique design and notable features of chiller mediate a large number of benefits for different industrial applications as given below:
- It feasibly addresses a cooling effect for a large-sized cooling application featured by multiple chilling system configurations. Total heat collected from the system is efficiently rejected in an environment configured by an air-cooled or water-cooled condenser.
- Different category compressors such as scroll/screw or centrifugal compressors provide variety to deal with different application requirements.
- Pressure is released from the condensed refrigerant to make it suitable for absorbing coolant heat by throttling /expansion valve.
- Discharged heat can be recovered to keep warm resorts or restaurants by integrating a heat pumping condenser. PHE provides a large surface area for efficient heat exchange between coolant and refrigerant, ensuring low space occupation.
- Control system installation prevents the unit from damage, increasing service life and durability for processing machines.
- Image Gallery
- Spare Parts
- Video
Why TopChiller is Your Reliable Chiller Manufacturer and Supplier In China?
Chiller-An Ultimate FAQ Guide by TopChiller
- What is a Chiller?
- What are the Main Components of a Chiller?
- What are Some Core Features of a Chiller?
- How Does a Chiller Work?
- What are the Advantages of Using a Chiller for your Industry?
- What is the Difference Between Vapor Compressor Chiller and Vapor Absorption Chiller?
- What are Vapor Compression Working Steps of a Chiller?
- How Many Types of Compressors are Used for Chiller?
- How Many Types of Chiller are Available Based on Condenser?
- What are the Prominent Applications of Chiller?
- What is Refrigerant Sub-Cooling and Superheating in a Chiller?
- What are Strategies for Energy Saving Operation of a Chiller?
- What is Series and Parallel Configuration of Chiller?
- What is the Heat Recovery System of a Chiller?
- Why is Corrosion Protection Important for your Chiller?
- Which Type of Heat Exchanger is Used for Chiller?
- Which Coils are Integrated With Shell & Tube Type Heat Exchanger of Chiller?
- Why is Glycol Important for Freezing Protection in your Chiller?
- What are Misconceptions About the Low Flow System of a Chiller?
- How to Select a Suitable Chiller for your Specific Application?
- How to Test the Operating Efficiency of your Chiller?
- How to Troubleshoot your Chiller?
What is a Chiller?
A Chiller is a steadfast working cooling unit that dissipates unwanted heat from processing applications and produces a cooling effect.
It ensures heat liberation either by a water-cooled condenser or air-cooled condenser. It is available with different cooling capacities and sizes.
The scroll/screw or centrifugal compressor is integrated depending on application requirements.
Environment-friendly behavior, different operating modes, and easy installation make it the best option for heat-generating systems.
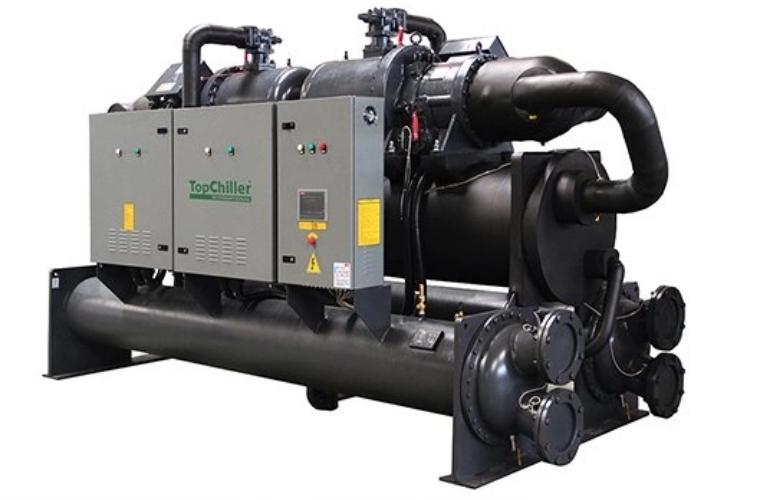

Highly Efficient Chiller Manufactured by TopChiller
What are the Main Components of a Chiller?
The essential components of the Chiller that are involved in its cooling operation are given below:
Compressor
The main component is mediated to make a pressure difference of refrigerant for its smooth flow throughout the refrigeration cycle.
There are different types of compressors with different cooling capacities as scroll/screw/centrifugal and reciprocating compressor etc.
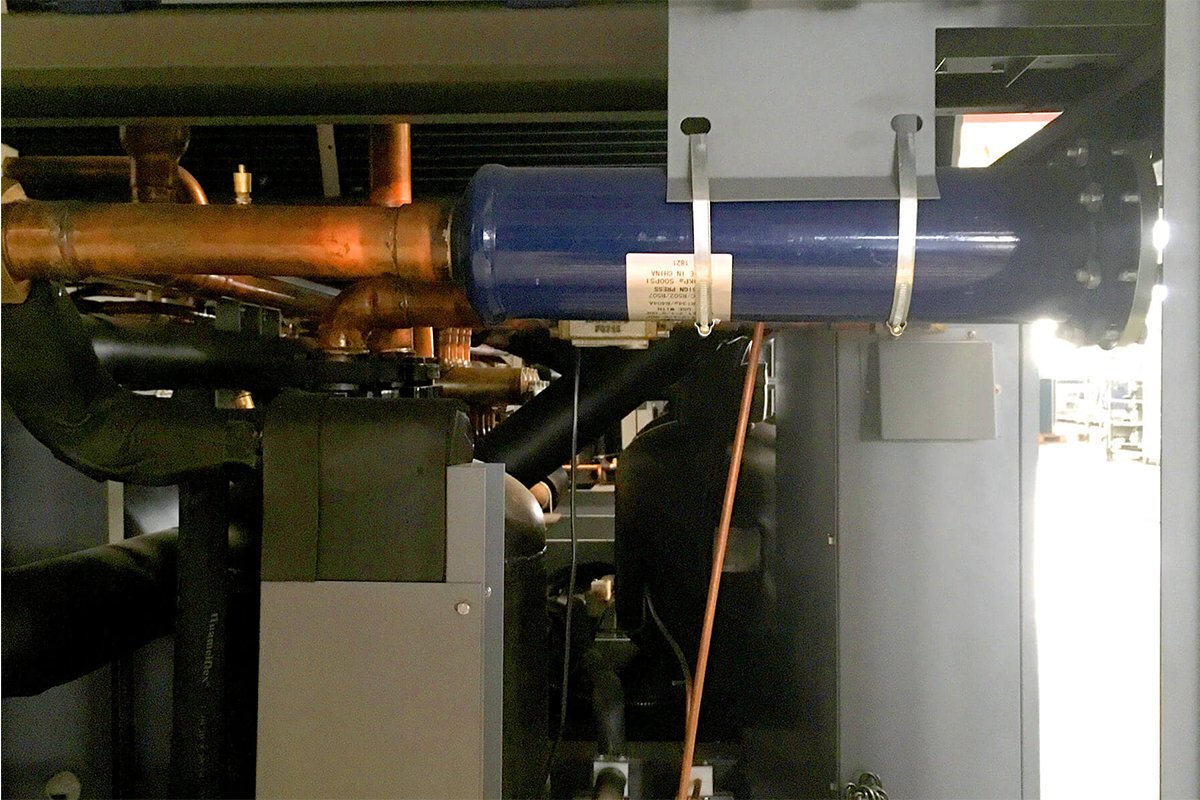
Condenser
After the compressor and the expansion valve, the condenser is integrated for receiving refrigerant. Its primary purpose is to cool the refrigerant by rejecting its heat.
Mainly condensers are of two types: an air-cooled condenser and a water-cooled condenser.
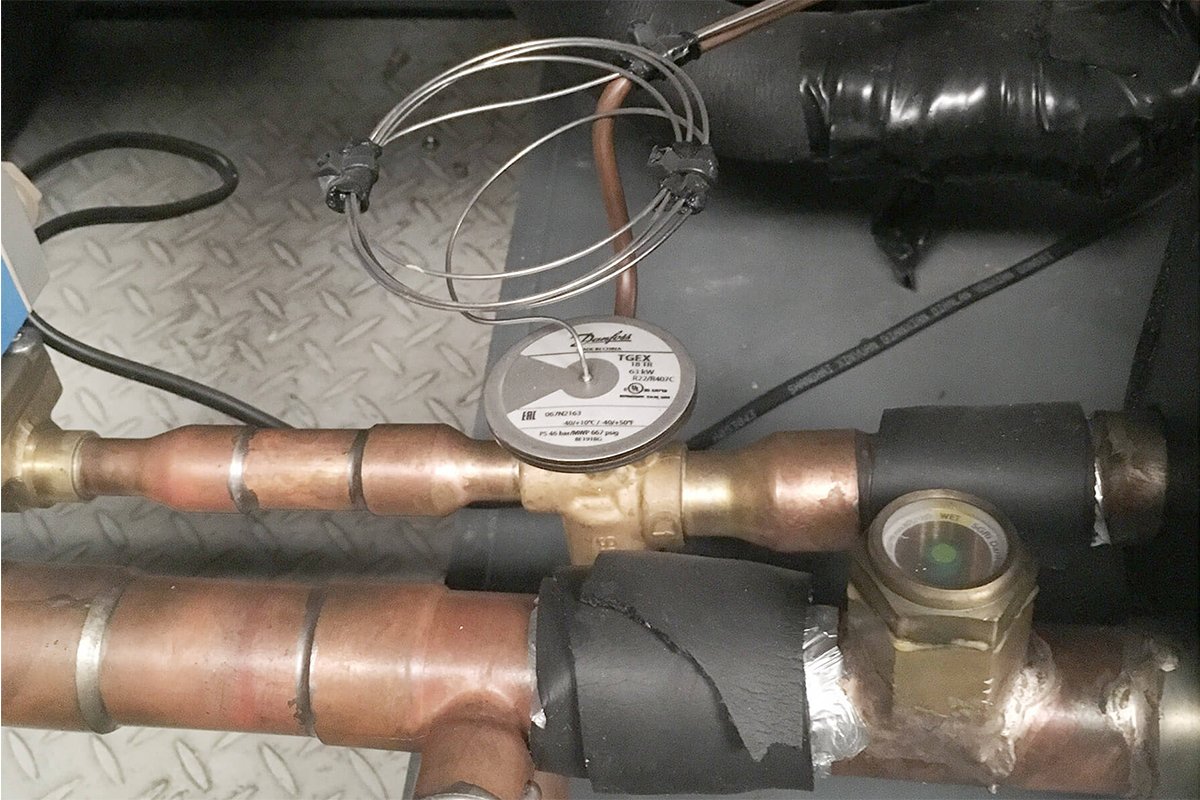
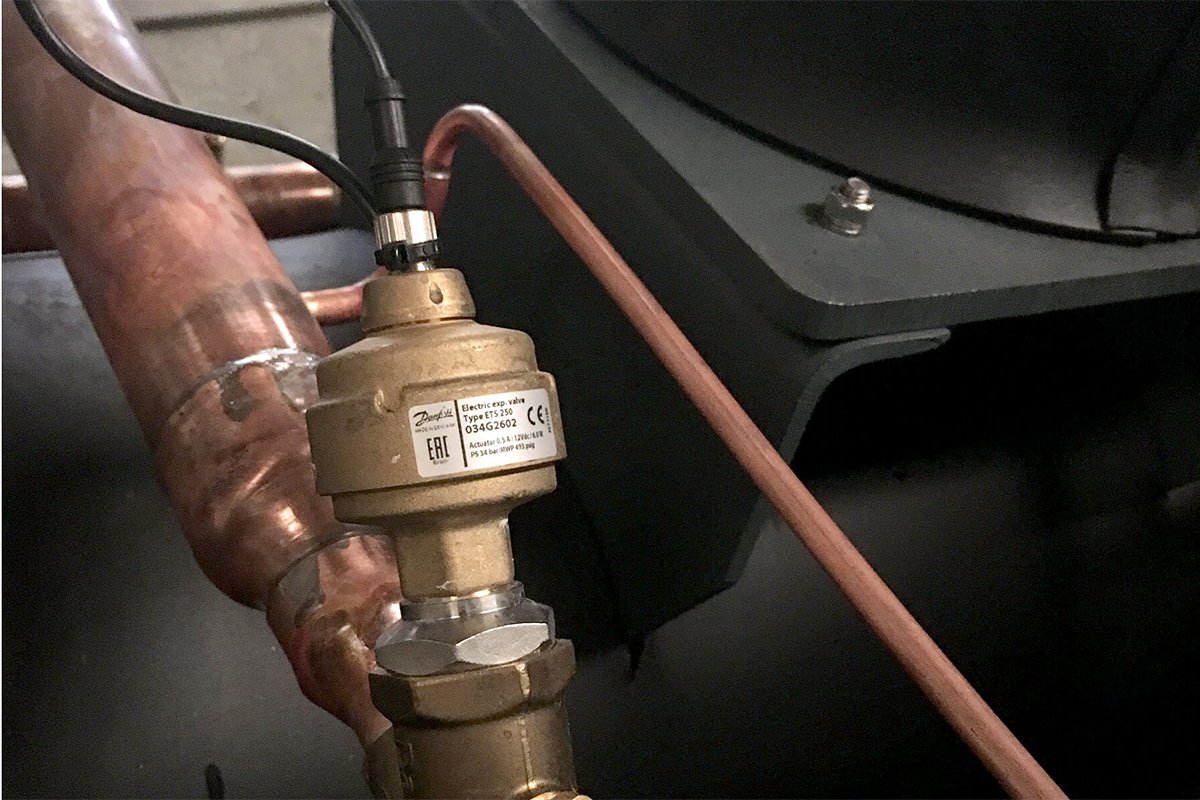
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is installed after the condenser which reduces the pressure of the refrigerant. As a result, the refrigerant volume increases for absorbing evaporator heat efficiently.
Expansion valves are also of two types thermal expansion vale and electronic expansion valves.
Evaporator
After pressure discharge, the refrigerant enters the evaporator. It collects all of the system heat through the refrigerant. Gaseous refrigerant finally dissipates heat by a cooling tower connected to condensers.
Power Unit
It is either directly connected to Chiller or put on the wall for providing an electric supply with voltage control.
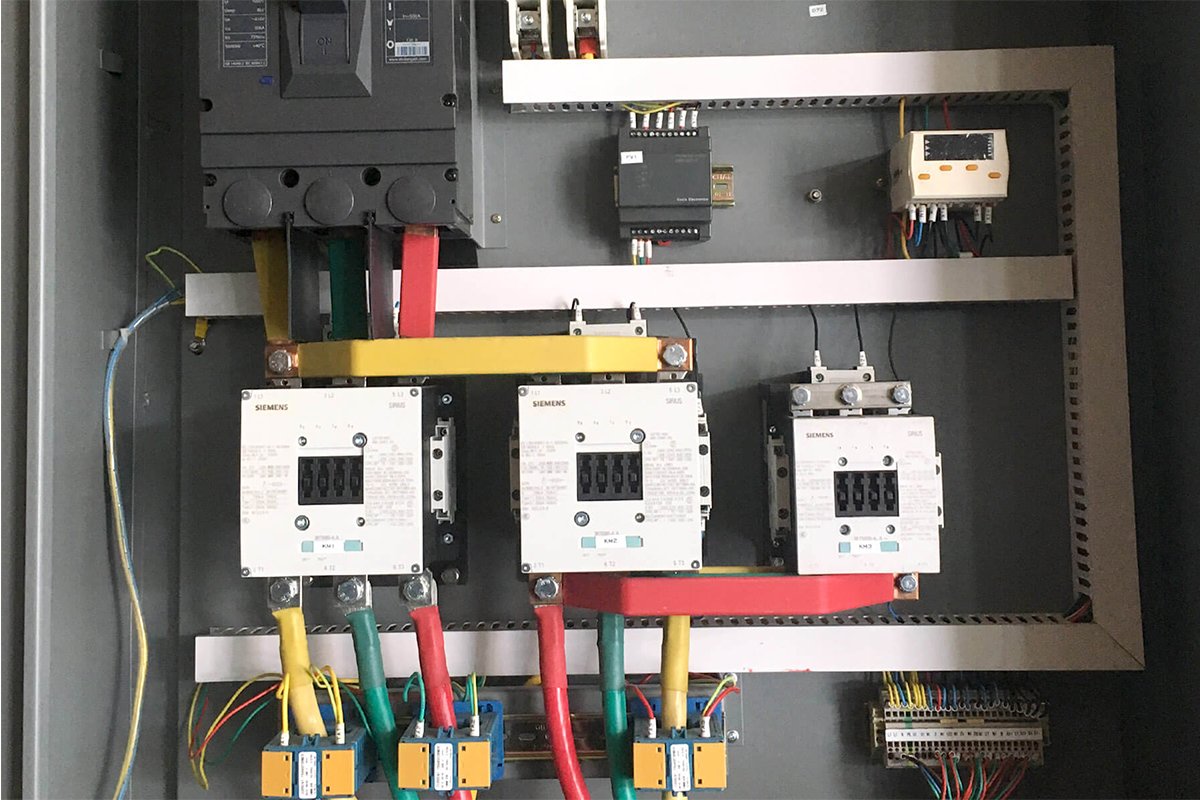
Controls
Different controls as a PLC-based microprocessor controller, switches, emergency alarms, and thermistors are integrated for safe and durable performance.
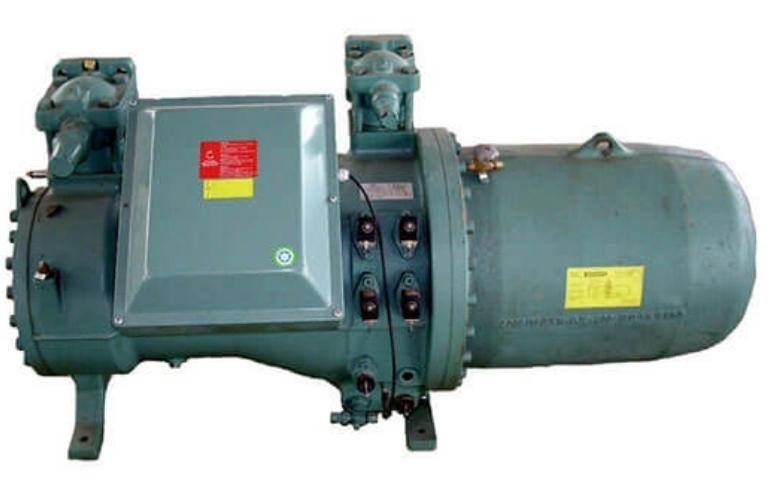

Explosion Proof Chiller Compressor
What are Some Core Features of a Chiller?
A Chiller executes cooling effect for different industrial applications under some core features as given below:
- Improved design compressor for quiet and energy-efficient operation with low power consumption.
- Air/water-cooled condensers for rejecting all of the wasted heat collected from the system.
- Integration of variable speed drives for capacity control of the compressor.
- Condenser fans for increasing water flow rate with no sound production.
- Variable speed drives connection with fans of condenser for energy-efficient and noise-free working.
- Reliable evaporator for heat exchange between refrigerant and coolant to ultimately cool the system.
- Condenser coils and evaporator coils are made of aluminum microchannel material for efficient heat exchange.
- Control units for reliable and regulated operation of the whole unit.
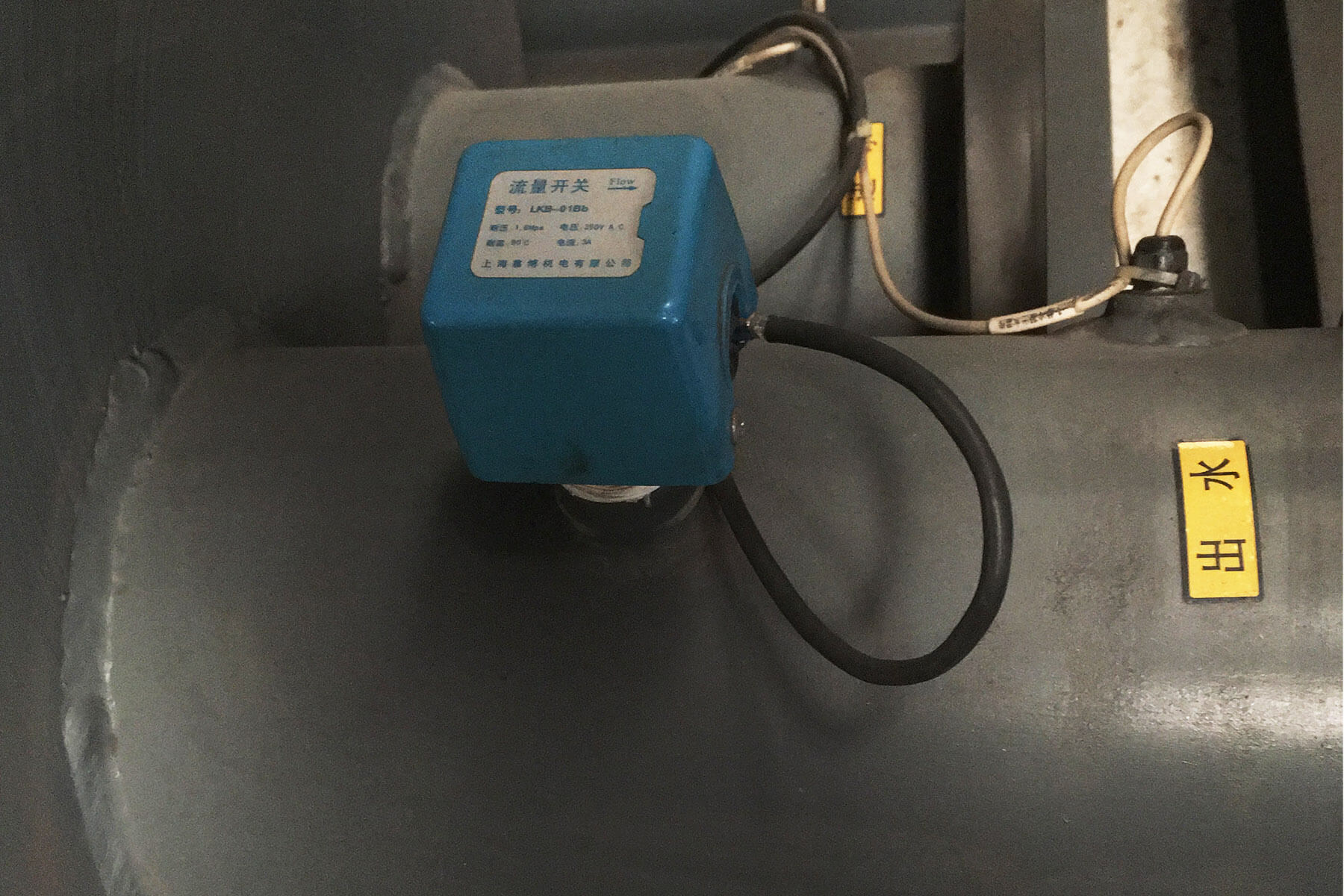
- Power supply with accurate voltage and flow switches for regulated operation.
- Environment friendly and corrosion resistive design for longer service life.
- Expansion valves to discharge pressure and increase the volume of refrigerant.
How Does a Chiller Work?
A Chiller is an energy-efficient unit that provides chilled water to cool a processing application. Its working steps are given below:
Step 1
Chilled water or glycol solution enters in processing application through a pumping system. The coolant circulates and absorbs all of the heat from the system resulting in the production of warm fluid.
Step 2
The warm fluid returns to Chiller and enters into the evaporator for heat transfer. The coolant is the main reservoir for transferring system heat to the unit.
Step 3
The refrigerant is installed that runs on compression and phase change principle. Processed water transfers its heat and boils refrigerant into gaseous form. The evaporated refrigerant with low pressure comes into the compressor.
Step 4
The compressor puts compression over low-pressure refrigerant and converts it into high-pressure refrigerant. Now the compressed refrigerant is ready to pass from discharge valves.
Step 5
High-pressure refrigerant finally enters the condenser for heat discharging. Heat is liberated from the refrigerant, condensing it into liquid through chilled water or ambient air circulation.
Step 6
High-pressure liquid refrigerant releases its pressure through expansion valves and enters into the evaporator to repeat the whole refrigeration cycle.
What are the Advantages of Using a Chiller for your Industry?
There are a diverse number of advantages to using a Chiller, as given below:
Equipment Protection
By its installation, different heat-producing machines are being protected from any damage. It dissipates heat feasibly from the system.
Reduction of Costs
The recirculating system prevents the water from being lost, resulting in preventing your costs consumption.
Long Service Life
Stainless steel and copper material are used for construction, increasing service life and durability.
Quiet Operation
Integration of vibration isolators and energy-efficient compressors ensures quiet and noise-free operation.
What is the Difference Between Vapor Compressor Chiller and Vapor Absorption Chiller?
Vapor Compressor Chiller
It works on the evaporation and compression principle. The compressor is used to compress the refrigerant and coolant for heat discharging from the system.
Vapor Compressor Chiller has rotating components. Vibration isolators are integrated with it to lessen vibration and noise production. The refrigeration cycle runs on the vapor compression principle and ultimately cools the system.
Vapor Absorption Chiller
The heat source is used for producing a cooling effect. But it does not use a compressor or fan for putting compression force over the refrigerant.
It has fewer rotating parts; therefore, it is a quiet and vibration-free operating unit. The working mechanism may contain lithium bromide as an absorbent and water refrigerant for producing chilled water.
What are Vapor Compression Working Steps of a Chiller?
The working steps of the vapor compression Chiller are given below:
Step 1
Water, air, or any other coolant enters an evaporator. The liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from it and covert in evaporated gas.
Step 2
Saturated and gaseous refrigerant does not increase its pressure and absorbs additional heat at constant pressure.
Step 3
Compressor sucked this evaporated refrigerant having low temperature and pressure. The compressor scrolls or rotors put compression over refrigerant increasing its temperature and pressure.
Step 4
The condenser makes sure to condense back gas into liquid refrigerant by rejecting its extra heat.
A throttling /expansion valve releases the pressure of the refrigerant, ready it again for collecting system heat.
No heat is exchanged in the expansion valve, but sometimes flash gas is produced that can be avoided by increasing the surface area of the condenser.
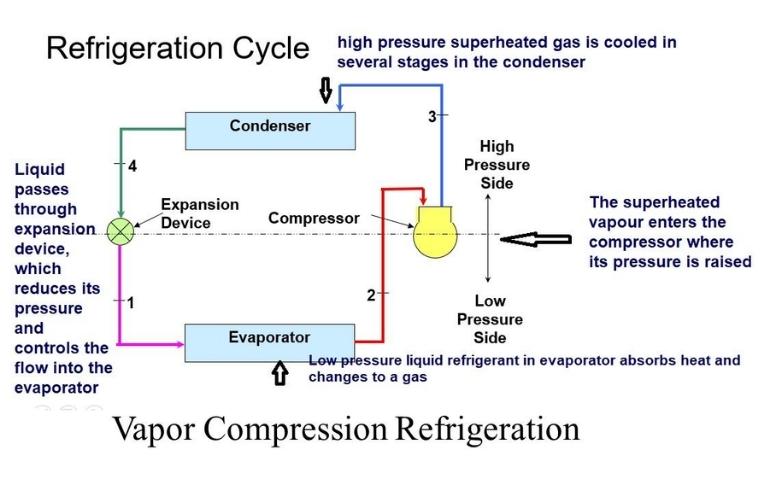
Vapor Compression Working Steps of a Chiller
How Many Types of Compressors are Used for Chiller?
There are different types of compressors having different capacities and working efficiency. Based on the application heat load, compressors are selected for Chiller as given below:
Scroll Compressor
Its main components involved in the operation are involute two scrolls. The upper scroll has a discharge port, while the bottom scroll is a rotating unit.
The orbiting motion of these scrolls assists in the suction, compression, and discharge of the refrigerant simultaneously.
Screw Compressor
The screw compressor also consists of two rotors. One is a female rotor containing gullies, while the male rotor consists of lobes.
The refrigerant is sucked towards the housing groove when rotors start rotation in opposite directions.
Compression occurs until rotors rotate and final transferring refrigerant at discharge line.
Centrifugal Compressor
In this compressor, the gaseous refrigerant is compressed centrifugally with increment in pressure and velocity.
It is mainly designed with a capacity ranges of 35 to 1000 tons. Centrifugal compressor is preferably used for Chiller with above 15-ton cooling capacity.
Reciprocating Compressor
It compresses the gaseous refrigerant with the piston of the cylinder. Refrigerant enters through the suction manifold and then in the compressor cylinder.
It is compressed here with a piston under pressure increment.
How Many Types of Chiller are Available Based on Condenser?
Based on the condenser, two types of Chiller are being used for cooling production in a specified application:
It consists of refrigeration circulation as well as water circulation for cooling. Ambient air is used to discharge the heat from the refrigerant.
Air circulates over condenser coils and absorbs heat from the compressed refrigerant. Exhaust heat is generated the use of exhaust equipment rejects that.
When it rains, the heat of vaporization is used in rainwater vaporization. As a result, the temperature drops to dissipate with air.
Hence, the efficiency of the regular operation increases in humidity instead of loss.
It also consists of both refrigeration as well as water circulation cycle. Water is used for application cooling while refrigerant provides a cooling effect for water coolant.
Gas refrigerant is being cooled and condensed by a water-cooled condenser. Chilled water comes from the cooling tower to condenser tubes and absorbs the heat from the refrigerant.
As a result, the refrigerant gets cooled and leaves the condenser. At the same time, hot water recovers its cooling from the cooling tower.
What are the Prominent Applications of Chiller?
For its substantial benefits, Chiller is widely installed for an assorted number of applications as given below:
- Injection Molding
- Blow Molding Machines
- Food and Beverage Industry
- Plastic Industry
- Pharmaceuticals
- Hospitals
- Medical Labs
- Lasers
- Chemical Industry
- Semiconductors
- Tool and Die Cutting
- Plating
- Rolling Mills
- Shopping Malls
- Offices
- Anodizing
- Concrete Industry
- Beer Brewing
What is Refrigerant Sub-Cooling and Superheating in a Chiller?
Sub-Cooling
Subcooling of the refrigerant occurs in Chiller before it enters the expansion valve. As a result, the evaporator capacity increases, and flash gas is not produced.
To prevent the refrigerant from sub-cooling, use a condenser with a high surface area for efficient heat exchange.
Superheating
Superheating occurs when the temperature of the refrigerant increases above of evaporation point. More significantly, the temperature of the refrigerant density will go down.
Ultimately mass flow rate and capacity of the compressor also slow down. Superheating occurs while superb cooling in the evaporator to the compressor.
The electronic expansion valves can mitigate superheating without liquid slugging to improve compressor working efficiency. Also, ensure that the suction lines are insulated to prevent refrigerants from overheating.
What are Strategies for Energy Saving Operation of a Chiller?
Some strategies for the energy-saving operation of Chiller are given below:
Heat Exchangers with Large Surface Area
Always select coils that provide a large surface area for heat exchange. The power consumption is lowered down by using efficient heat exchangers.
Prevent the Usage of Air Cooled Condenser
Air-cooled condensers are used for low heat loads. To benefit from wet-bulb temperature with low power utilization, always install water cooled Chiller.
Use of Outside Air
If the ambient temperature is favorable, increase its use for energy-saving heat discharge.
Installation of Control System
Install the control system to identify the best energy-efficient operating mode and prevent the Chiller from high power consumption.
Defrosting
The flow rate decreases by the accumulation of frosts in the evaporator, and power consumption increases. Use warm air around evaporator or thermal heaters for frost prevention.
Prevent Oil from Overcharging
Make sure that the oil level in the compressor may remain at a set point. An increase or decrease in oil level can cause problems, either leakage or reducing the heat exchanging process of the evaporator with power consumption.
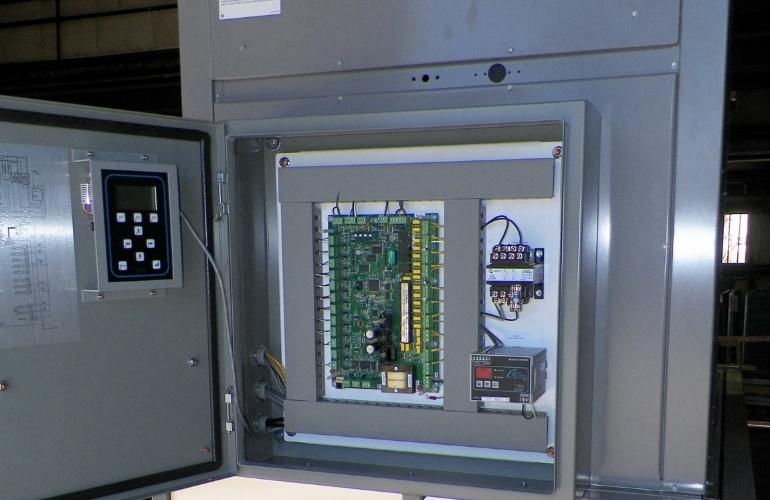

Quick Responsive Chiller Control System
What is Series and Parallel Configuration of Chiller?
Multiple systems are preferably used when the chilling system is required to deal with the high heating load. The multiple units are arranged either in parallel or series configurations.
Parallel Configuration
Two or more chilling units are connected in a parallel configuration having the same cooling tower. Defects in one unit may decrease the overall working efficiency.
Series Configuration
All chilling units are arranged head to head for series configuration. Each Chiller is integrated with a separate pumping system. It resolves the problem that occurs by parallel configuration.
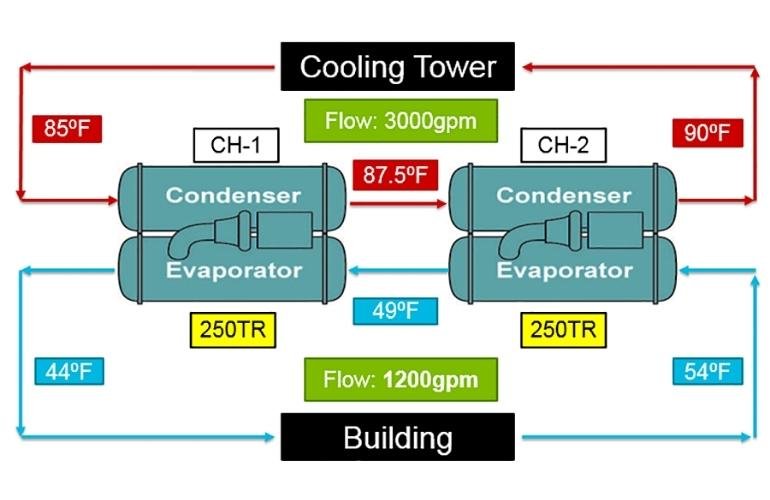
Series Configuration Strategy of Chiller
What is the Heat Recovery System of a Chiller?
A heat recovery system is beneficial for applications requiring chilling and heating effects. The Chiller can work both on heating and cooling mode.
In this system, heat discharged from the condenser is being absorbed by water and restored through a water pump.
This recovered heat is spread for warmth, especially in resorts, hotels, etc. Heat recovery condensers or heat pumping condensers are used for this purpose.
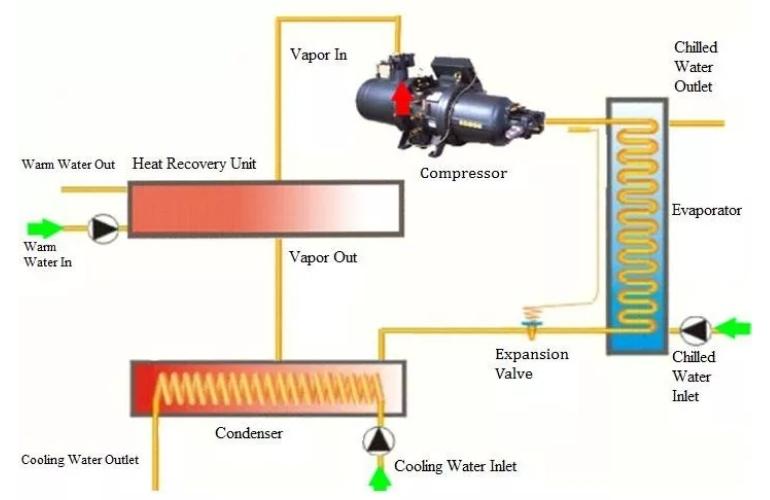
Heat Recovery System of a Chiller
Why is Corrosion Protection Important for your Chiller?
Importance of Corrosion Protection
A Chiller is a cooling unit featured with a condenser and evaporator. Environmental factors can affect badly on condenser coils.
Rusting not only occurs in industrial and marine areas, but rural or urban areas’ environments can also cause corrosion effects.
Corrosion also depends on material quality. If the material is not good quality, the rusting process will be fast—a rapid pitting attack over coils resulting in catastrophic refrigerant leakage.
Premature corrosion in evaporator or condenser coils may cause performance degradation, leaks, and ultimately unit failure.
Therefore for efficient cooling performance, there is a need for corrosion protection.
Strategies for Corrosion Protection
When choosing Chiller, always consider material quality. Coils designed with good material show corrosion resistance.
Copper coils and aluminum fins with epoxy coating provide significant protection against corrosion.
Before stamping, pre-coated condenser coils have more outstanding superb durability but not for extreme industrial environments.
Which Type of Heat Exchanger is Used for Chiller?
Shell and Tube Type Heat Exchanger
It consists of several convoluted tubules surrounded by a sturdy shell. For increasing the surface area of the heat exchanger, the number of tubes can be increased.
The coolant flows either in a shell or in the tubing of the heat exchanger.
Heat is being exchanged between the refrigerant and coolant fluid. Consequently, the hot refrigerant leaves the evaporator, enters into the surge drum, and then into the compressor. It occupies a larger surface as compared to the PHE.
PHE
The plate heat exchanger consists of plates and convoluted tubing interspersed on plates. The refrigerant flows in the tubing while the coolant plates for heat exchange.
It is easy to install and maintain for its low internal volume for the refrigerant. It occupies less space, ensuring quick heat exchange.
PHE is considered to be more efficient in performance as compared to shell and tube type heat exchangers.
Plates are arranged in similar manners, increasing surface areas for heat exchange.
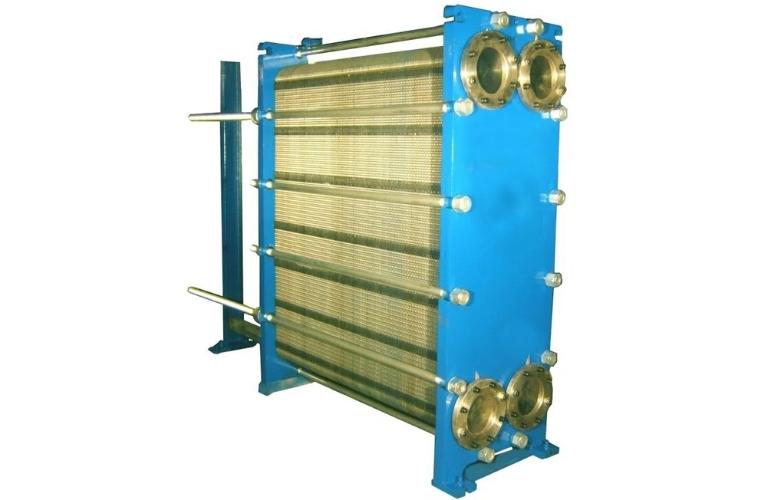

Corrosion Resistant Chiller Heat Exchanger
Which Coils are Integrated With Shell & Tube Type Heat Exchanger of Chiller?
Shell and tube type is configured with two design coils as given below:
Direct Expansion Coils
These coils of shell and tube type evaporator mediate the direct release of refrigerant for entering the compressor.
Condensed refrigerant coming from condensers enters in direct expansion coils of the heat exchanger through an expansion valve.
Heat exchange takes place, and refrigerant converts in a gaseous state. The compressor sucks the evaporated liquid to imply compression force.
Flooded Type Coils
These coils are flooded with refrigerant that enters the shell through a surge drum or pumping. The flooded refrigerant absorbs heat from the coolant circulating in coils and gets heat up.
The evaporated refrigerant then enters in surge drum. The compressor sucks the gas refrigerant from the drum instead of direct sucking it from the heat exchanger.

Anti Rust Chiller Coils
Why is Glycol Important for Freezing Protection in your Chiller?
Glycol is an important freezing agent that can prevent refrigerants from freezing. It is crucial to use glycol in applications installed outside at low ambient temperature.
Some Chiller needs low temperature than that freezing point. For this, glycol is mixed in water to decrease its freezing point. The percentage concentration of glycol mixing in water depends upon the need for temperature fall.
Mainly it is available in two types ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. For food-related applications, propylene glycol is preferred use because of its non-toxic behavior.
While ethylene glycol is installed for industrial applications, glycol has excellent importance for freezing protection in the evaporator, preventing the unit from clogging and overall damage.
What are Misconceptions About the Low Flow System of a Chiller?
There are some misconceptions about the low flow rate as given below:
- It is perceived that a low flow rate system is best suitable if the piping system is extended.
- It is also said that a low flow rate system would be only productive for the advent chilled water system.
- Only specified Chiller designed by some specified manufacturers works on this low flow system, not all.
By making an inspection, it was proved that all the above are misconceptions. For example, the low flow system is also suitable for short piping as for long piping.
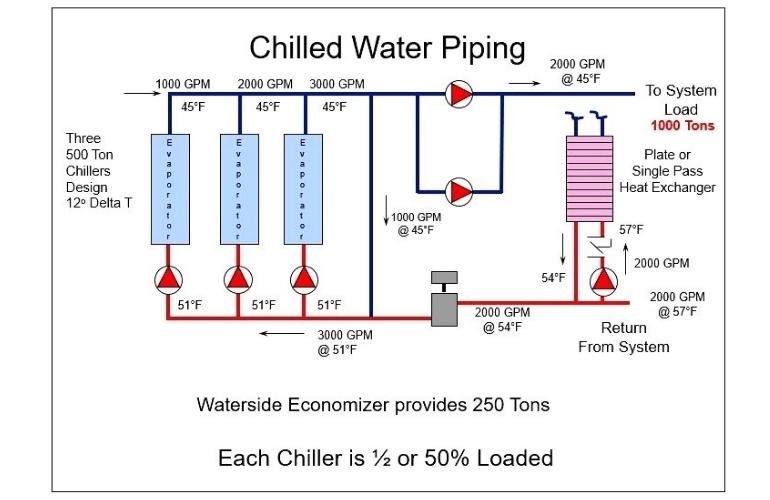
Chiller Piping System Diagram
How to Select a Suitable Chiller for your Specific Application?
A Chiller is specified for cooling operation, and it is available with different cooling capacities. It can be selected by following some parameters as given below:
- By calculating the heating load of the required application, the unit should be selected.
- The installation site is also considered a low ambient temperature and high temperature.
- For an environment with a high temperature, a Water Chiller is used. While for lower ambient temperature, an Air Chiller is preferably selected.
- Waste energy economics and water flow rate are also compared with application requirements.
- For the temperature lower than 20⁰C in the evaporator, the unit with a two-stage compression system is preferably installed. For temperature below 50⁰C in the evaporator, a cascade system is installed.
- Also, consider the type of refrigerant. Choose environment-friendly and ozone protective refrigerant.
Chiller Evaporator
How to Test the Operating Efficiency of your Chiller?
Some considerations should be kept in mind for estimating the working efficiency of the Chiller as given below:
Clean Tubing
As heat exchangers provide a cool fluid for cooling of application. By placing any obstruction or hurdle in the heat exchanger, diminish in flow rate and working efficiency can be determined.
So make sure to clean the tubing of the heat exchanger regularly and prevent it from rusting.
Daily Logs
Inspect the working operation and make daily records. Note down flow rate, pressure, and temperature of the refrigerant.
Compare the whole week’s performance record. If you find a decrease in operation efficiency, replace that component or amend the problem for efficient working.
Refrigerant Leakage
Cooling capacity decreases due to refrigerant leakage or the addition of moisture in the refrigerant.
Check out all valves and piping of refrigerant to find leakage. Repair the damage for efficient working.
Glycol Concentration
Low ambient temperature cause freezing of water in the refrigerant. The temperature of the coolant should always be lower than the freezing point. So first, check out the ambient temperature and mix glycol in water accordingly.
The average concentration of glycol increases the working efficiency of the evaporator by preventing the unit from freezing.
Water Flow
Measure the water flow rate by using a flow meter. If it would be less than 2-3 GPM per ton, make adjustments and increase the flow rate for quick operation.
How to Troubleshoot your Chiller?
Chiller is fabricated with branded components and stainless steel material for durable and efficient working.
But sometimes, errors may occur in its operation. Errors and their troubleshooting steps are given below:
1-Oil Clogging
Gasoline leakage from compressor causes it’s transferring to condenser and filters by the refrigerant.
When oil gets mixed with refrigerant, it causes blockage in the refrigerant flow because of its high viscosity.
Troubleshooting
This problem is sorted out by replacing the filters with a new one. The unit will start working by preventing oil leakage and using the dryer to heat the condenser.
2-Ice Blockage
If there is high moisture in the Water Chiller, the moisture gets concentrated gradually in the throttle outlet. Ultimately it’s got frozen at the throttle, causing a blockage in operation.
Troubleshooting
The problem is troubleshot by evacuation of the whole refrigeration cycle. Moisture presence is determined by a water indicator that turns green.
The regular operation is started by replacing oil, refrigerator, and evacuating all components.
3-High Condensing pressure
Sometimes pressure increases due to high refrigerant charge, condenser lower space, or high-pressure setpoints.
Troubleshooting
The problem is sorted out by replacing the small surfaced condenser with a larger one by resetting the pressure requirements and checking the charge of the refrigerant.